I would like to
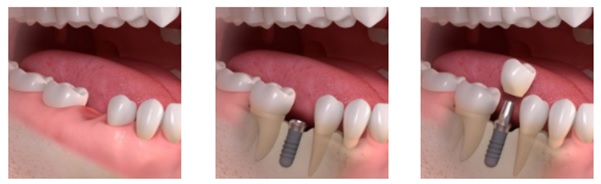
Implant patients are of all ages and implants may be the right choice for anyone missing one or more teeth due to injury, disease or decay. They are especially practical for patients who can no longer wear removable dentures. Dr Patel can determine if you are a candidate for dental implants after a careful evaluation of your dental and medical history. The main condition is to have the bone in good condition. Some contraindications should be noted: patients with heart disease, renal failure, smoking, hypertension, and uncontrolled diabetes. A CBCT scan may be required to assess the bone quantity.
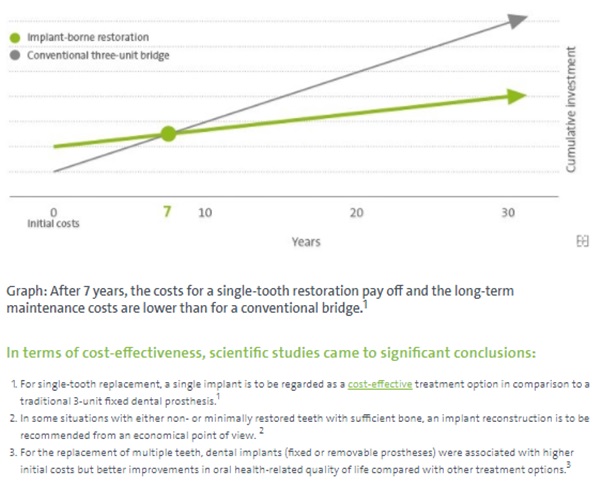
It is important for a patient to have enough bone to support the implant. If you do not have enough bone, there are many safe and effective ways to correct bone deficiency. Following tooth extraction the extraction site undergoes bone resorption. 30%-50% of bone can be resorped within the first 6 months of extraction depending on patients age. It is important that implants are placed during this period before further loss of bone. Failure to do this will require extra surgical procedures to increase volume of bone available for implant placement.
After tooth extraction, the alveolar ridge will commonly decrease in volume and change morphologically. These changes are usually clinically significant and can make placement of a conventional bridge or an implant-supported crown difficult. If bone resorption is significant enough, then placement of an implant may become extremely challenging. Postextraction maintenance of the alveolar ridge minimizes residual ridge resorption and, thus, allows placement of an implant that satisfies esthetic and functional criteria. 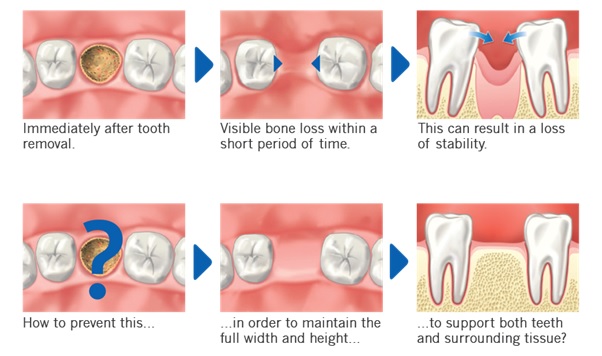
This is a surgical procedure designed to to increase the amount of tooth available to crown a tooth that has suffered extensive loss of its structure. It involved removing gum tissue, bone or both to expose more of a tooth. 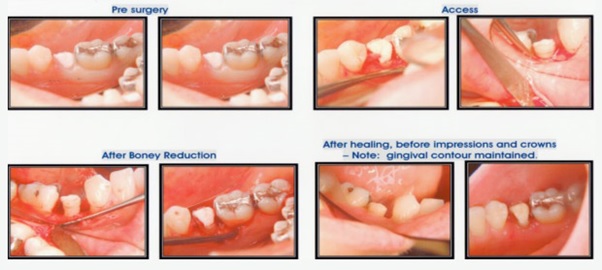
A gingival graft, also called gum graft. Is a surgical procedure with the aim to cover exposed root surfaces caused by recession. 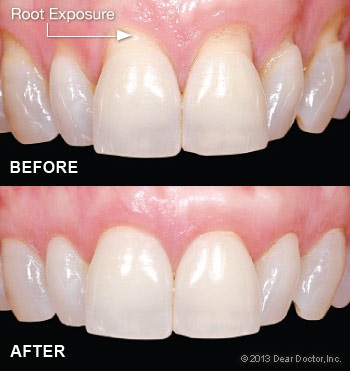
Hemisection dental Surgery is a procedure in which a tooth with two roots is cut in half. This procedure may be needed when there is bone loss, or dental decay between the roots, due to gum (periodontal) disease or one of the roots root canal fillings has failed. The root that is saved is the prepared for a crown about 6 weeks after the failed portion has been removed. 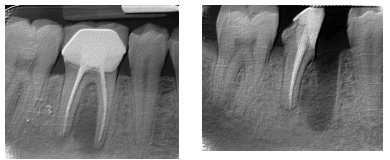
Is an endodontic surgical procedure whereby a tooth’s root tip is removed and a root end cavity is prepared and filled with a biocompatible material. 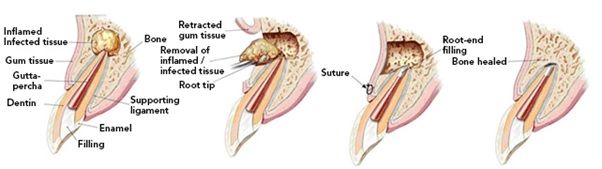
In the upper arch, the tissue that connects the gum to the lip is called the labial frenum. If it is abnormally wide or long, it may connect through to the gum tissue between the teeth and extend to the front portion of the roof of the mouth. When the upper frenum is too wide or long, it can create a space between the two front teeth. 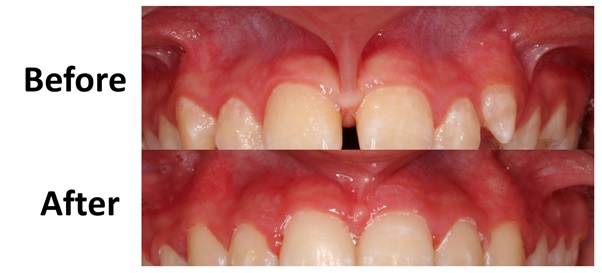 For more information, or to book a consultation, please click here or call 01296 398 180.
For more information, or to book a consultation, please click here or call 01296 398 180.


Over the counter cosmeceutical skincare products might moisturise the top layer of the skin but they are unlikely to reverse any ageing process at the cellular level.
READ MORE